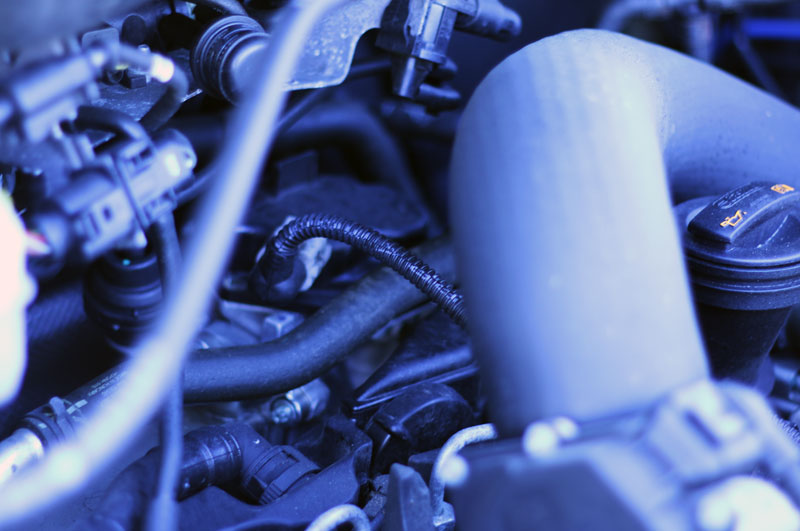
Many car owners often wonder about the specific technologies powering their vehicles, and whether their engine is equipped with a turbocharger is a common question. Understanding if your car has this component can provide valuable insights into its performance characteristics, maintenance requirements, and overall driving dynamics. A turbocharger is a forced induction device that increases an internal combustion engine’s efficiency and power output by forcing extra air into the combustion chamber. This guide will help you definitively determine if your vehicle benefits from this ingenious piece of engineering, exploring various methods from visual checks to performance observations.
Decoding the Signs: How to Identify a Turbocharged Engine
Determining whether your car is turbocharged involves a combination of visual inspections, auditory checks, and an understanding of its driving characteristics. Each method offers distinct clues that, when combined, can provide a clear answer.
Visual Inspection: Under the Hood Clues
The most direct way to check for a turbocharger is to look under the hood. While engine layouts vary significantly, certain components are tell-tale signs of a turbocharged system. A careful examination can reveal these crucial parts.
- The Turbocharger Unit: Look for a snail-shaped device bolted to the engine’s exhaust manifold. It typically has two main sections: the turbine housing (connected to the exhaust) and the compressor housing (connected to the intake).
- Intercooler: Turbochargers heat the air as they compress it. To cool this air before it enters the engine, an intercooler is often present. This radiator-like component is usually located at the front of the car, behind the grille, or sometimes mounted on top of the engine.
- Specific Piping: You’ll notice thicker, often metallic or reinforced rubber pipes connecting the turbocharger to the intercooler, and from the intercooler to the engine’s intake manifold. These pipes are designed to handle pressurized air.
- Wastegate or Blow-off Valve: These components are related to turbo operation. A wastegate controls exhaust gas flow to the turbine, while a blow-off valve (or diverter valve) releases excess pressure when the throttle closes.
Auditory Cues: Listening for the Whistle
Beyond visual confirmation, a turbocharged engine often produces distinctive sounds that are absent in naturally aspirated engines. These sounds are most noticeable during acceleration or when letting off the throttle.
Listen for a subtle, high-pitched “whistle” or “spooling” sound as the engine revs up, particularly under moderate to hard acceleration. This is the turbocharger’s turbine spinning rapidly. When you quickly lift your foot off the accelerator, especially after boosting, you might hear a “hiss” or “whoosh” sound, which is the blow-off valve releasing excess pressure.
Driving Experience: Feel the Boost
The way a car drives can also provide strong indications of turbocharging. Turbocharged engines deliver power differently than their naturally aspirated counterparts.
You might notice a slight delay in power delivery when you first press the accelerator, often referred to as “turbo lag.” However, once the turbo spools up, there’s usually a noticeable surge of power, often feeling like a strong push as the boost kicks in. Turbocharged engines also tend to produce significant torque at lower RPMs compared to a similarly sized naturally aspirated engine.
Checking Your Car’s Documentation and Specifications
If visual and auditory checks are inconclusive or challenging, the most reliable methods involve consulting official documentation or online resources. Your car’s owner’s manual is an invaluable source of information, explicitly detailing engine specifications and features. Similarly, checking the vehicle’s specification sheet, often found on the manufacturer’s website by inputting your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number), will clearly state whether your engine is turbocharged. Many online car databases also allow you to search for your specific make, model, and year to review its factory specifications.
Turbocharged vs. Naturally Aspirated Engines
Understanding the fundamental differences between these two engine types can further aid in identifying which one powers your vehicle.
| Feature | Turbocharged Engine | Naturally Aspirated Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Power Output | Higher power-to-displacement ratio (more power from smaller engine) | Power scales with engine size (larger engine for more power) |
| Fuel Efficiency | Potentially better due to downsizing and optimized combustion (especially at lower loads) | Generally less efficient for equivalent power output |
| Engine Sound | Often has a distinct whistle or spooling sound | Smoother, more linear sound without forced induction noises |
| Power Delivery | Lag followed by a surge of power (boost) | Linear and immediate power delivery across RPM range |
| Complexity | More complex due to additional components (turbo, intercooler, extra piping) | Simpler design, fewer moving parts related to air induction |
Advantages of Turbocharging
The widespread adoption of turbochargers in modern vehicles is driven by several compelling benefits they offer:
- Increased Power Output: A smaller engine can produce significantly more horsepower and torque than a naturally aspirated engine of the same size, leading to better acceleration and performance.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: By allowing manufacturers to use smaller engines (engine downsizing) that produce comparable power to larger naturally aspirated engines, turbochargers can contribute to better fuel economy, especially during normal driving conditions.
- Reduced Emissions: More efficient combustion and smaller engine displacements often lead to lower carbon dioxide and other harmful emissions, helping vehicles meet stricter environmental standards.
- Better Performance at Altitude: Turbochargers compensate for the thinner air at higher altitudes by forcing more air into the engine, maintaining power output where naturally aspirated engines would struggle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a turbocharger?
A turbocharger is an exhaust gas-driven forced induction device that increases an engine’s power output by compressing the air entering the engine. It uses the waste energy from exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which in turn spins a compressor, forcing more air into the cylinders.
Can I add a turbo to my car?
Write a quality, in-depth, magazine-style article on the topic:
Write in English
Use a clickbait and catchy headline. Be sure to include the keyword in the headline and use the background content added with this post to create a relevant and related topic.
Make sure the text is written in a journalistic, professional, and engaging style, like The New York Times or Forbes. The tone should be optimistic, forward-looking, and persuasive. Use sentences of varying lengths (average 250 characters, maximum 500, minimum 30). Use appropriate analogies, descriptive adverbs (e.g., “incredibly effective”), and correct adverbial phrases (e.g., “By integrating insights from AI…”). Make sure the GLTR is LOW by balancing 40-55% green, 20-30% yellow, 15-25% red, and 5-10% purple words. Use present and past participles to add dynamism. Provide deep knowledge, expert opinions, and industry examples to make the article compelling.
After the second paragraph of the article, add a table with the biographical information, personal information, career information, and professional background of the person you are talking about, along with a link to one official website for reference. The table should be in a format that is easy to embed in WordPress.
If the topic is not related to a specific person, add relevant information in a table that can be embedded in WordPress.
Ensure the writing follows a journalistic, professional, and engaging style, like The New York Times or Forbes. The tone should be optimistic, forward-looking, and persuasive. Use varied sentence lengths (average 250 characters, max 500, min 30). Incorporate relatable analogies, descriptive adverbs (e.g., ‘remarkably effective’), and proper adverbial phrases (e.g., ‘By integrating AI-driven insights…’). Ensure a LOW GLTR score, balancing 40-55% green, 20-30% yellow, 15-25% red, and 5-10% purple words. Use present and past parts to enhance dynamism. Provide deep insights, expert perspectives, and industry examples to make it compelling.
After the second paragraph of the article add table with bio data and personal information, career, professional information of person in topic, also add link to one authentic website for reference, the table should be in the form that it can be easily inserted in wordpress.
If the topic is other than person related than add related information in the form of table that can be inserted in wordpress.
While technically possible, adding a turbocharger to a naturally aspirated car is a complex and expensive modification. It requires extensive changes to the engine’s fuel system, cooling system, exhaust, and engine management unit (ECU) tuning. It’s best performed by experienced professionals and is often not recommended for daily drivers due to potential reliability issues and cost.
Are turbocharged engines less reliable?
Modern turbocharged engines are designed for high reliability, but they can be more sensitive to maintenance and operating conditions than naturally aspirated engines. Proper oil changes with the correct type of oil, careful warm-up and cool-down procedures, and avoiding excessive stress are crucial for their longevity.
How do I maintain a turbocharged engine?
Key maintenance practices include using high-quality synthetic engine oil and adhering strictly to manufacturer-recommended oil change intervals. Allowing the engine to warm up before driving hard and letting it cool down for a minute or two after strenuous driving can prevent oil coking in the turbo’s bearings. Regular checks of the air filter and intercooler for blockages are also important.
Ultimately, knowing whether your car has a turbocharger empowers you with a deeper understanding of its engineering and performance capabilities. By utilizing visual inspections, listening for tell-tale sounds, feeling its unique power delivery, and consulting official documentation, you can confidently determine your vehicle’s setup. This knowledge is not just for curiosity; it aids in proper maintenance, understanding its performance characteristics, and making informed decisions about its care. Drive safely and enjoy the unique characteristics of your engine, whatever its configuration.